Detailed information on BSc in Cyber Security

A Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in Cyber Security is an undergraduate degree program that focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. This program equips students with the knowledge and skills needed to identify vulnerabilities, prevent attacks, and respond to security breaches. Here are some key aspects of a typical B.S. in Cyber Security program:
Core Subjects
- Fundamentals of Cyber Security: Introduction to the basics of cyber security, including key concepts and terminology.
- Networking: Study of computer networks, network protocols, and network security.
- Operating Systems: Understanding the security features and vulnerabilities of various operating systems.
- Cryptography: Techniques for securing information through encryption and decryption.
- Ethical Hacking: Learning to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in a controlled and ethical manner to improve security.
- Digital Forensics: Techniques for investigating cyber incidents and analyzing digital evidence.
- Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating risks to an organization's information assets.
- Security Policies and Compliance: Developing and enforcing policies to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Software Security: Ensuring that software applications are designed and implemented securely.
- Incident Response: Planning and executing responses to cyber incidents and breaches.
Skills Acquired
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in various programming languages, knowledge of network configurations, and familiarity with security tools and software.
- Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze security threats, assess risks, and develop strategies to counteract them.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Creative and logical approaches to identifying and solving security issues.
- Communication Skills: Effectively communicating security policies, procedures, and risks to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Ethical Judgment: Understanding the ethical implications of cyber security practices and adhering to legal standards.
Career Opportunities
Graduates with a B.S. in Cyber Security can pursue various career paths, such as:
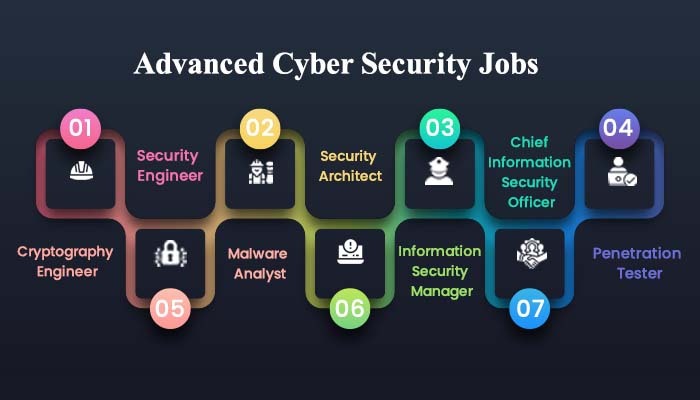
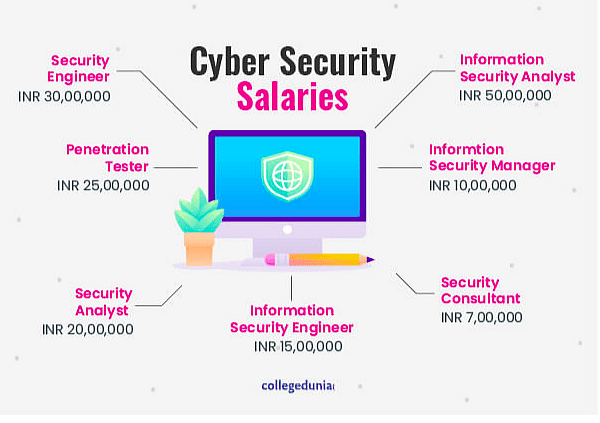
- Cyber Security Analyst: Monitoring and protecting an organization's networks and systems from cyber threats.
- Network Security Engineer: Designing and implementing secure network solutions.
- Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker): Identifying vulnerabilities in systems and networks by simulating cyber attacks.
- Security Consultant: Advising organizations on best practices for securing their information systems.
- Digital Forensics Analyst: Investigating cyber crimes and analyzing digital evidence.
- Incident Response Specialist: Managing and mitigating the effects of security breaches.
Certifications
Many cyber security professionals enhance their credentials with certifications such as:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
Program Formats
- On-Campus: Traditional classroom-based learning.
- Online: Flexible, internet-based courses that can be completed remotely.
- Hybrid: A combination of on-campus and online coursework.
A B.S. in Cyber Security provides a solid foundation for individuals seeking to enter the rapidly growing field of cyber security, with a focus on protecting digital assets and maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information systems.