What is a proxy server ?
A proxy server is an intermediary server that sits between a client (such as a computer or mobile device) and the internet. It facilitates requests from the client to various online resources, and then returns the requested information back to the client. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of its functions and uses:

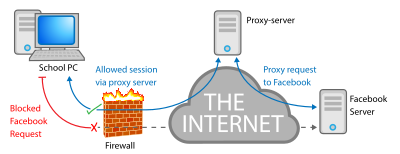
Key Functions of a Proxy Server:
-
Anonymity:
- IP Masking: The proxy server hides the client’s IP address, providing a level of anonymity.
- Privacy: By masking the IP address, the proxy server helps protect the client’s privacy.
-
Security:
- Firewall: It can act as a firewall, filtering out harmful content and preventing unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Some proxy servers can encrypt data, adding a layer of security to communications.
-
Content Filtering:
- Parental Controls: It can block access to certain websites based on predefined criteria.
- Company Policies: Businesses use proxy servers to enforce internet usage policies.
-
Caching:
- Speed: By caching frequently accessed web pages and resources, a proxy server can reduce load times.
- Bandwidth Savings: It reduces bandwidth consumption by serving cached content.
-
Access Control:
- Authentication: Proxy servers can require users to authenticate before granting internet access.
- Usage Monitoring: They can log user activities for monitoring and auditing purposes.
Types of Proxy Servers:
-
Forward Proxy:
- Usage: Typically used by clients to access the internet. Common in business environments to control and monitor employee internet usage.
- Example: A company uses a forward proxy to filter employee internet access.
-
Reverse Proxy:
- Usage: Typically used by servers to manage incoming requests. It hides the details of the backend servers.
- Example: A web server uses a reverse proxy to balance load among multiple backend servers.
-
Transparent Proxy:
- Usage: Intercepts requests without modifying them. The client is unaware of the proxy.
- Example: Used in public Wi-Fi hotspots to filter content.
-
Anonymous Proxy:
- Usage: Hides the client’s IP address but identifies itself as a proxy.
- Example: Used to bypass geographical restrictions while maintaining some level of anonymity.
-
High Anonymity Proxy (Elite Proxy):
- Usage: Completely hides the fact that it is a proxy and the client’s IP address.
- Example: Used for maximum anonymity and to bypass severe internet censorship.
Benefits of Using a Proxy Server:
- Improved Security: Protects against threats and unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Privacy: Masks IP addresses and encrypts data.
- Access Control: Regulates internet usage and enforces policies.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Caches data to save bandwidth and speed up access.
- Bypass Restrictions: Access geographically restricted or blocked content.
Conclusion:
Proxy servers play a crucial role in enhancing privacy, security, and efficiency in internet usage. They are versatile tools used in various contexts, from individual users seeking anonymity to enterprises managing extensive networks.