Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subfield of Artificial intelligence
"Learning machines to imitate human intelligence"
Machine Learning (ML)
Traditional programming uses algorithms to produce results from data:
Data + Algorithms = Results
Machine learning creates algorithms from data and results:
Data + Results = Algorithms
Neural Networks (NN)
Neural Networks is:
- A programming technique
- A method used in machine learning
- A software that learns from mistakes
Neural Networks are based on how the human brain works:
Neurons are sending messages to each other. While the neurons are trying to solve a problem (over and over again), it is strengthening the connections that lead to success and diminishing the connections that lead to failure.
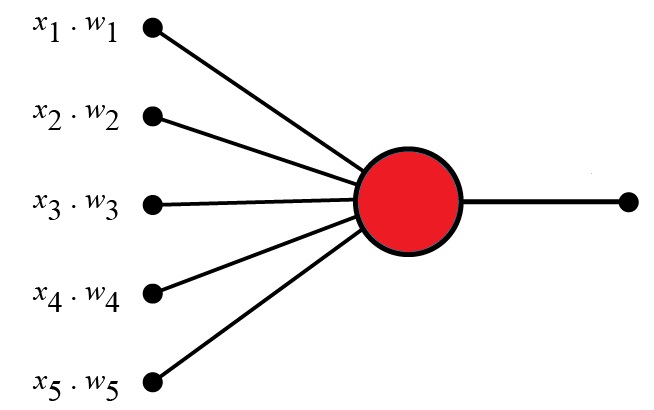
Perceptrons
The Perceptron defines the first step into Neural Networks.
It represents a single neuron with only one input layer, and no hidden layers.
Neural Networks
Neural Networks are Multi-Layer Perceptrons.
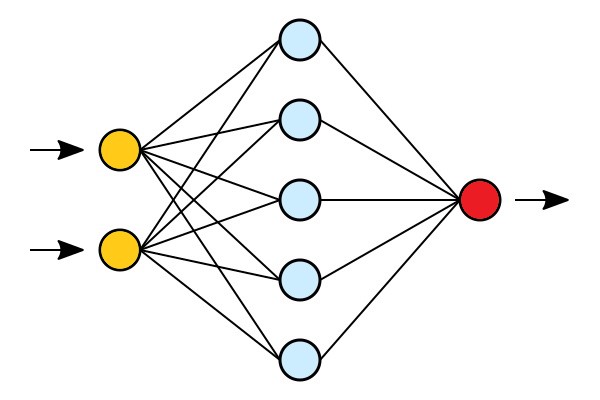
In its simplest form, a neural network is made up from:
- An input layer (yellow)
- A hidden layer (blue)
- An output layer (red)
In the Neural Network Model, input data (yellow) are processed against a hidden layer (blue) before producing the final output (red).
The First Layer:
The yellow perceptrons are making simple decisions based on the input. Each single decision is sent to the perceptrons in the next layer.
The Second Layer:
The blue perceptrons are making decisions by weighing the results from the first layer. This layer make more complex decisions at a more abstract level than the first layer.
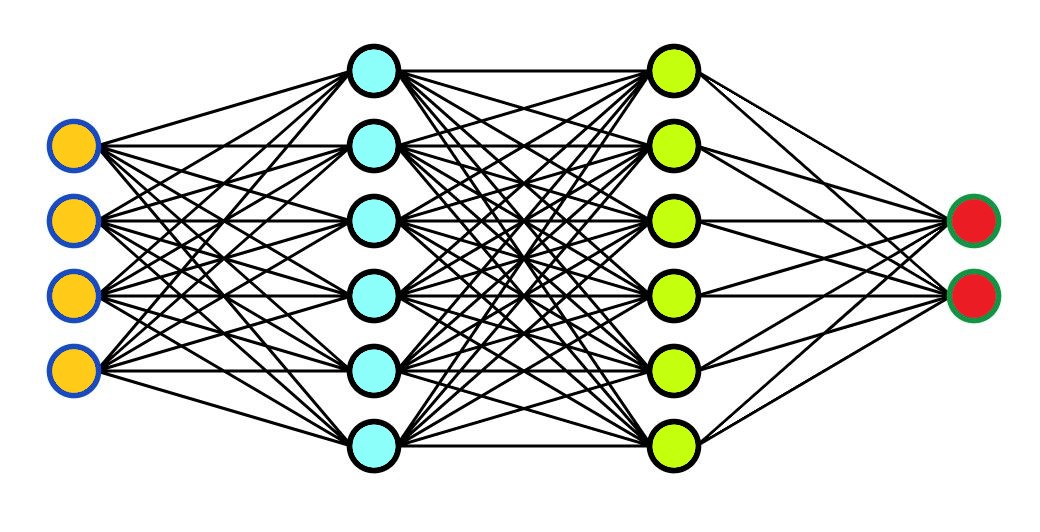
Deep Neural Networks
Deep Neural Networks are made up of several hidden layers of neural networks that perform complex operations on massive amounts of data.
Each successive layer uses the preceding layer as input.
For instance, optical reading uses low layers to identify edges, and higher layers to identify letters.
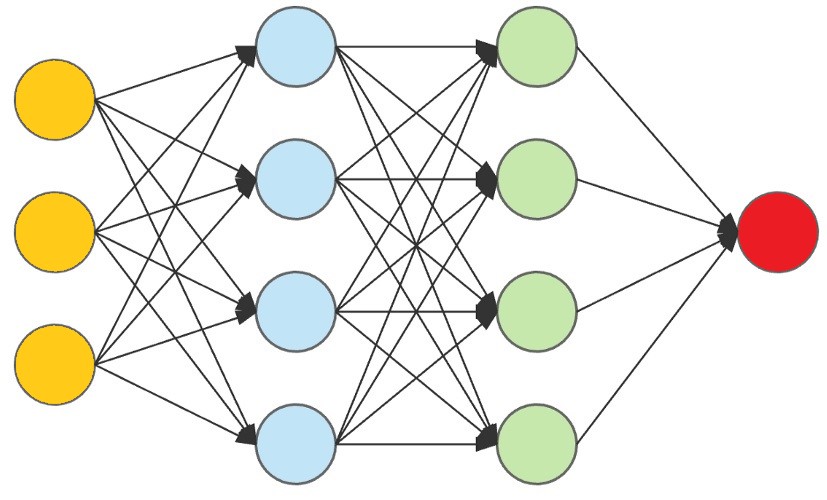
In the Deep Neural Network Model, input data (yellow) are processed against a hidden layer (blue) and modified against more hidden layers (green) to produce the final output (red).
The First Layer:
The yellow perceptrons are making simple decisions based on the input. Each single decision is sent to the perceptrons in the next layer.
The Second Layer:
The blue perceptrons are making decisions by weighing the results from the first layer. This layer make more complex decisions at a more abstract level than the first layer.
The Third Layer:
Even more complex decisions are made by the green perceptrons.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning.
Deep Learning is responsible for the AI boom of the last years.
Deep learning is an advanced type of ML that handles complex tasks like image recognition.
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|
| A subset of AI | A subset of Machine Learning |
| Uses smaller data sets | Uses larger datasets |
| Trained by humans | Learns on its own |
| Creates simple algorithms | Creates complex algorithms |
Artificial Intelligence
Is a Contrast to
Human Intelligence
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence suggest that machines can mimic humans in:
- Talking
- Thinking
- Learning
- Planning
- Understanding
Artificial Intelligence is also called Machine Intelligence and Computer Intelligence.
Arthur Samuel 1959:
"Machine Learning is a subfield of computer science that gives computers the ability to learn without being programmed"
Arthur Samuel, IBM Journal of Research and Development, Vol. 3, 1959.
Wikipedia 2022:
Artificial intelligence is intelligence demonstrated by machines. Unlike natural intelligence displayed by humans and animals, which involves consciousness and emotionality.
Investopedia 2022:
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
IBM 2022:
Artificial intelligence leverages computers and machines to mimic the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of the human mind.
Britannica 2022:
Artificial intelligence is the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings, .... such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from past experience.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
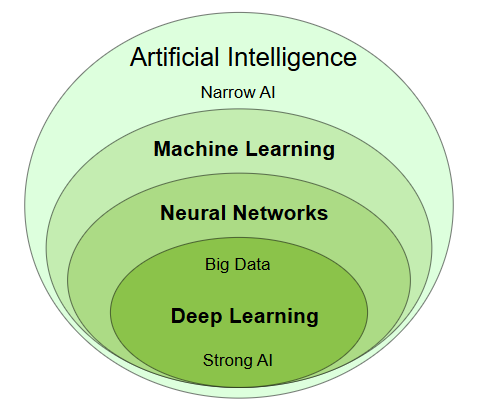
Artificial Intelligence is a scientific discipline embracing several Data Science fields ranging from narrow AI to strong AI, including machine learning, deep learning, big data and data mining.
Narrow AI
Narrow Artificial Intelligence is limited to narrow (specific) areas like most of the AI we have around us today:
- Email spam Filters
- Text to Speech
- Speech Recognition
- Self Driving Cars
- E-Payment
- Google Maps
- Text Autocorrect
- Automated Translation
- Chatbots
- Social Media
- Face Detection
- Visual Perception
- Search Algorithms
- Robots
- Automated Investment
- NLP - Natural Language Processing
- Flying Drones
- IBM's Dr. Watson
- Apple's Siri
- Microsoft's Cortana
- Amazon's Alexa
- Netflix's Recommendations
Narrow AI is also called Weak AI.
Weak AI: Built to simulate human intelligence.
Strong AI: Built to copy human intelligence.
Strong AI
Strong Artificial Intelligence is the type of AI that mimics human intelligence.
Strong AI indicates the ability to think, plan, learn, and communicate.
Strong AI is the theoretical next level of AI: True Intelligence.
Strong AI moves towards machines with self-awareness, consciousness, and objective thoughts.
✔ One need not decide if a machine can "think".
One need only decide if a machine can act as intelligently as a human.
Alan Turing