C Get Started
Get Started With C
To start using C, you need two things:
- A text editor, like Notepad, to write C code
- A compiler, like GCC, to translate the C code into a language that the computer will understand
There are many text editors and compilers to choose from. In this tutorial, we will use an IDE (see below).
C Install IDE
An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is used to edit AND compile the code.
Popular IDE's include Code::Blocks, Eclipse, and Visual Studio. These are all free, and they can be used to both edit and debug C code.
Note: Web-based IDE's can work as well, but functionality is limited.
We will use Code::Blocks in our tutorial, which we believe is a good place to start.
You can find the latest version of Codeblocks at http://www.codeblocks.org/. Download the mingw-setup.exe file, which will install the text editor with a compiler.
C Quickstart
Let's create our first C file.
Open Codeblocks and go to File > New > Empty File.
Write the following C code and save the file as demo.c (File > Save File as):
demo.c
int main() {
printf("Hello World!");
return 0;
}
Don't worry if you don't understand the code above - we will discuss it in detail in later chapters. For now, focus on how to run the code.
In Codeblocks, it should look like this:
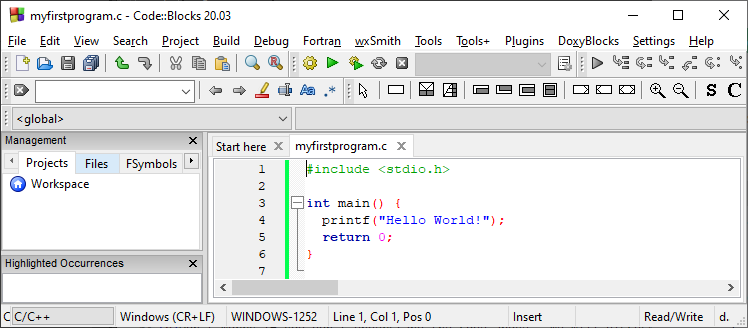
Then, go to Build > Build and Run to run (execute) the program. The result will look something to this:
Hello World!
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.011 s
Press any key to continue.Congratulations! You have now written and executed your first C program.
demo.c
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello World!");
return 0;
}
Result:
Hello World!