- Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
- HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
HTML Editors
A simple text editor is all you need to learn HTML.
Step 1: Open TextEdit (Mac)
Open Finder > Applications > TextEdit
Also change some preferences to get the application to save files correctly. In Preferences > Format > choose "Plain Text"
Then under "Open and Save", check the box that says "Display HTML files as HTML code instead of formatted text".
Then open a new document to place the code.
Step 2: Write Some HTML
Write or copy the following HTML code into Notepad:
Step 3: Save the HTML Page
Save the file on your computer. Select File > Save as in the Notepad menu.
Name the file "index.htm" and set the encoding to UTF-8 (which is the preferred encoding for HTML files).
Tip: You can use either .htm or .html as file extension. There is no difference; it is up to you.
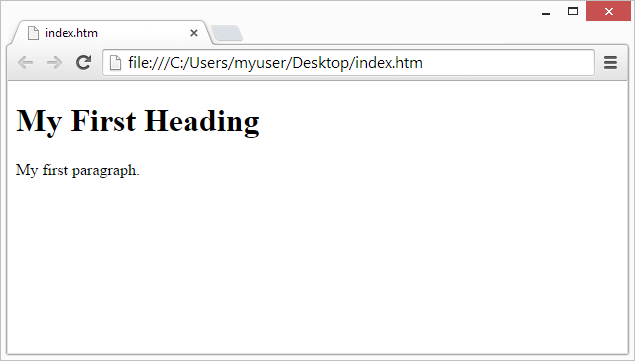
Step 4: View the HTML Page in Your Browser
Open the saved HTML file in your favorite browser (double click on the file, or right-click - and choose "Open with").